Page 148 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 148
122 Membranesfor Industrial Wastewater Recoverg and Re-use
250
200
150
100
50
0
0.6 1.6 2.2 2.9
Amplitude, cm
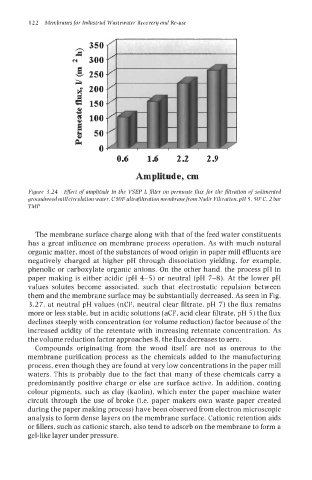
Figure 3.24 Efefert of amplitude in the VSEP L filter on permeate flux for the filtration of sedimented
groundwood mill circulation water. C30F ultrafiltration membrane from Nadir Filtration, pH 5, 50"C, 2 bar
TMP
The membrane surface charge along with that of the feed water constituents
has a great influence on membrane process operation. As with much natural
organic matter, most of the substances of wood origin in paper mill effluents are
negatively charged at higher pH through dissociation yielding, for example,
phenolic or carboxylate organic anions. On the other hand, the process pH in
paper making is either acidic (pH 4-5) or neutral (pH 7-8). At the lower pH
values solutes become associated, such that electrostatic repulsion between
them and the membrane surface may be substantially decreased. As seen in Fig.
3.27, at neutral pH values (nCF, neutral clear filtrate, pH 7) the flux remains
more or less stable, but in acidic solutions (aCF, acid clear filtrate, pH 5) the flux
declines steeply with concentration (or volume reduction) factor because of the
increased acidity of the retentate with increasing retentate concentration. As
the volume reduction factor approaches 8, the flux decreases to zero.
Compounds originating from the wood itself are not as onerous to the
membrane purification process as the chemicals added to the manufacturing
process, even though they are found at very low concentrations in the paper mill
waters. This is probably due to the fact that many of these chemicals carry a
predominantly positive charge or else are surface active. In addition, coating
colour pigments, such as clay (kaolin), which enter the paper machine water
circuit through the use of broke (i.e. paper makers own waste paper created
during the paper making process) have been observed from electron microscopic
analysis to form dense layers on the membrane surface. Cationic retention aids
or fillers, such as cationic starch, also tend to adsorb on the membrane to form a
gel-like layer under pressure.