Page 144 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 144
118 Membranes for lndustrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-use
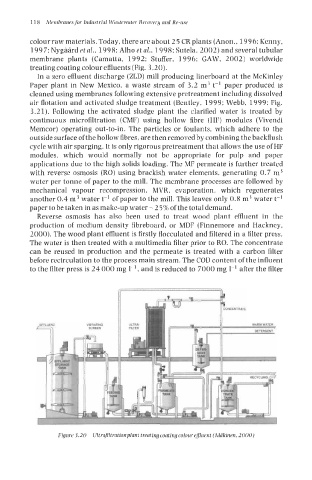
colour raw materials. Today, there are about 25 CR plants (Anon., 1996: Kenny,
1997: Nygiird Pt al., 1998: Alho et al., 1998; Sutela, 2002) and several tubular
membrane plants (Camatta, 1992: Stuffer, 1996: GAW, 2002) worldwide
treating coating colour effluents (Fig. 3.20).
In a zero effluent discharge (ZLD) mill producing linerboard at the McKinley
Paper plant in New Mexico, a waste stream of 3.2 m3 t-I paper produced is
cleaned using membranes following extensive pretreatment including dissolved
air flotation and activated sludge treatment (Bentley, 1999: Webb, 1999: Fig.
3.21). Following the activated sludge plant the clarified water is treated by
continuous microfiltration (CMF) using hollow fibre (HF) modules (Vivendi
Memcor) operating out-to-in. The particles or foulants, which adhere to the
outside surface of the hollow fibres, are then removed by combining the backflush
cycle with air sparging. It is only rigorous pretreatment that allows the use of HF
modules, which would normally not be appropriate for pulp and paper
applications due to the high solids loading. The MF permeate is further treated
with reverse osmosis (RO) using brackish water elements, generating 0.7 m3
water per tonne of paper to the mill. The membrane processes are followed by
mechanical vapour recompression, MVR, evaporation, which regenerates
another 0.4 m3 water t-' of paper to the mill. This leaves only 0.8 m3 water t-'
paper to be taken in as make-up water - 2 5% of the total demand.
Reverse osmosis has also been used to treat wood plant effluent in the
production of medium density fibreboard, or MDF (Finnemore and Hackney,
2000). The wood plant effluent is firstly flocculated and filtered in a filter press.
The water is then treated with a multimedia filter prior to RO. The concentrate
can be reused in production and the permeate is treated with a carbon filter
before recirculation to the process main stream. The COD content of the influent
to the filter press is 24 000 mg I-l, and is reduced to 7000 mg 1-1 after the filter
I I_ ~ I - --_
Figure 3.20 Ultrujltratmnplnnt treatingcoating colour efluent (Mbkinen, 2000)