Page 140 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 140
114 Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recoverg arid Reuse
BREF stipulates, amongst other things, permitted effluent loads and, for the first
time, effluent flows for different kinds of pulp and paper mills. The directive also
includes a list of candidate techniques and practises (under BAT, best available
technology, Tables 3.16 and 3.17) recognised as being able to achieve the
mandatory effluent loads.
The effluent loads allowed according to the IPPC directive are extremely
rigorous. In particular, target levels for nitrogen and phosphorus cannot be
achieved by use of conventional external (end-of-pipe) biological treatment
alone. The allowed effluent flows, on the other hand, necessitate counter current
water circulation systems and internal water recycling, also stated in the IPPC
directive and aimed at minimising freshwater consumption.
The focus of the internal water purification used today has been mainly on the
removal of suspended solids by mechanical filtration (e.g. disc filter), flotation or
chemical precipitation. Flotation (or flotation combined with sand filtration, so-
called flotation filtration) has been successfully used to remove suspended solids
and to recover fibres, fillers and fines from the white water. However, flotation
tanks generally demand a lot of floor space and the process is fairly energy
intensive. The cost and the filtrate quality are very dependent on the chemicals
used, which are usually expensive. Flotation is used to a large extent in mills
using recovered paper as raw material. Chemical precipitation is also used
within the paper machine white water treatment system. The aim is to improve
the first-pass retention in the wire section and, at the same time, the suspended
solids content is reduced in the white water. However, chemicals are usually
expensive and the doses required can be large. Moreover, overdosing of
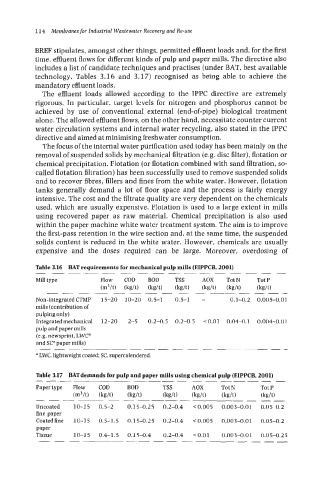
Table 3.16 BAT requirements for mechanical pulp mills (EIPPCB. 2001)
Non-integratedCTMP 15-20 10-20 0.5-1 0.5-1 - 0.1-0.2 0.005-0.01
mills (contribution of
pulping only)
Integratedmechanical 12-20 2-5 0.2-0.5 0.2-0.5 < 0.01 0.04-0.1 0.004-0.01
pulp and paper mills
(e.g. newsprint, LWC"
and SCB paper mills)
a LWC, lightweight coated SC, supercalendered.
Table 3.17 BATdemands for pulp and paper mills using chemical pulp (EIPPCB, 2001)
Papertype Plow COD BOD TSS AOX Tot N Tot P
(m3/t) (kdt) (kdt) (kg/t) (kg/t) (kg/t) (kg/t)
Uncoated 10-15 0.5-2 0.15-0.25 0.2-0.4 <0.005 0.003-0.01 0.05-0.2
fine paper
Coatedfine 10-15 0.5-1.5 0.15-0.25 0.2-0.4 <0.005 0.003-0.01 0.05-0.2
paper
Tissue 10-15 0.4-1.5 0.15-0.4 0.2-0.4 <0.01 0.003-0.01 0.05-0.25