Page 137 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 137
Industrial waters 11 1
Table 3.13 Consumption and emission levels of the biggest non-integrated wood-free fine
paper mill in Europe and a typical tissue mill (EIPPCB, 2001)
Wood-free 6 4.5 0.44, 0.11, 7, 0.14, 41.9.2 3.0.8
fine paper 97 24 0.15 30 (inorganic)
Tissue 7-100 6-100 2-6" 1-2" 5-15" 1-3a 6-100a 1-30"
mill (total)
a After wastewater treatment plant.
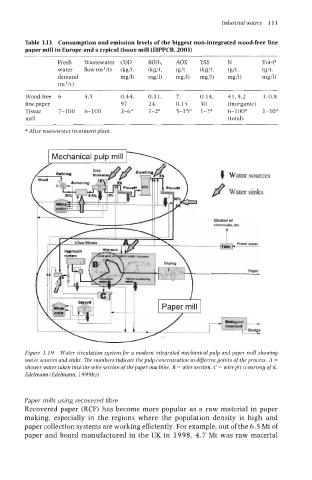
Figure 3.19 Water circulation system for a modern integrated mechanical pulp and paper mill showing
water sources and sinks. The numbers indicate the pulp concentration in different points of the process. A =
shower water taken into the wire section of the paper machine, R = wire section, C = wire pit (courtesy of K.
Edelmann (Edelmann, 1999b))
Paper mills using recovered fibre
Recovered paper (RCF) has become more popular as a raw material in paper
making, especially in the regions where the population density is high and
paper collection systems are working efficiently. For example, out of the 6.5 Mt of
paper and board manufactured in the UK in 1998, 4.7 Mt was raw material