Page 132 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 132
Industrial waters 10;
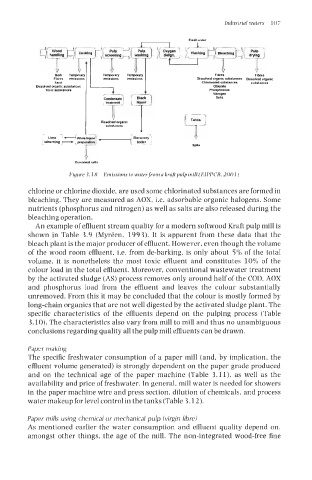
Pigrire 3. I8 Emissions to waterfroni a kruftpulp mill (GIPPCB. 2001)
chlorine or chlorine dioxide, are used some chlorinated substances are formed in
bleaching. They are measured as AOX, i.e. adsorbable organic halogens. Some
nutrients (phosphorus and nitrogen) as well as salts are also released during the
bleaching operation.
An example of effluent stream quality for a modern softwood Kraft pulp mill is
shown in Table 3.9 (Myreen, 1993). It is apparent from these data that the
bleach plant is the major producer of effluent. However, even though the volume
of the wood room effluent, i.e. from de-barking, is only about 5% of the total
volume, it is nonetheless the most toxic effluent and constitutes 10% of the
colour load in the total effluent. Moreover, conventional wastewater treatment
by the activated sludge (AS) process removes only around half of the COD, AOX
and phosphorus load from the effluent and leaves the colour substantially
unremoved. From this it may be concluded that the colour is mostly formed by
long-chain organics that are not well digested by the activated sludge plant. The
specific characteristics of the effluents depend on the pulping process (Table
3.10). The characteristics also vary from mill to mill and thus no unambiguous
conclusions regarding quality all the pulp mill effluents can be drawn.
Paper making
The specific freshwater consumption of a paper mill (and, by implication, the
effluent volume generated) is strongly dependent on the paper grade produced
and on the technical age of the paper machine (Table 3.11), as well as the
availability and price of freshwater. In general, mill water is needed for showers
in the paper machine wire and press section, dilution of chemicals, and process
water makeup for level control in the tanks (Table 3.12).
Paper mills using chemical or mechanical pulp (virgin fibre)
As mentioned earlier the water consumption and effluent quality depend on,
amongst other things, the age of the mill. The non-integrated wood-free fine