Page 161 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 161
lndwtrial waters 13 5
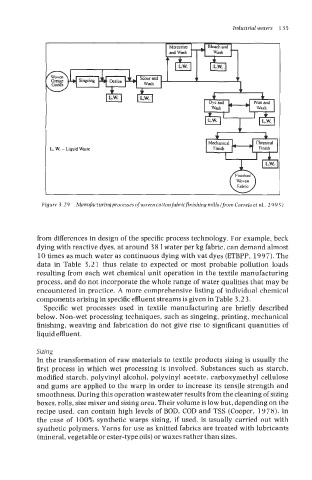
Woven
Fabnc
Figure 3.29 Manufacturingprocesseuofwovencottonfabricfinishing mills (from Correiaet al.. 199 5)
from differences in design of the specific process technology. For example, beck
dying with reactive dyes, at around 38 1 water per kg fabric, can demand almost
10 times as much water as continuous dying with vat dyes (ETBPP, 1997). The
data in Table 3.21 thus relate to expected or most probable pollution loads
resulting from each wet chemical unit operation in the textile manufacturing
process, and do not incorporate the whole range of water qualities that may be
encountered in practice. A more comprehensive listing of individual chemical
components arising in specific effluent streams is given in Table 3.2 3.
Specific wet processes used in textile manufacturing are briefly described
below. Non-wet processing techniques, such as singeing, printing, mechanical
finishing, weaving and fabrication do not give rise to significant quantities of
liquid effluent.
Sizing
In the transformation of raw materials to textile products sizing is usually the
first process in which wet processing is involved. Substances such as starch,
modified starch, polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinyl acetate, carboxymethyl cellulose
and gums are applied to the warp in order to increase its tensile strength and
smoothness. During this operation wastewater results from the cleaning of sizing
boxes, rolls, size mixer and sizing area. Their volume is low but, depending on the
recipe used, can contain high levels of BOD, COD and TSS (Cooper, 19 78). In
the case of 100% synthetic warps sizing, if used, is usually carried out with
synthetic polymers. Yarns for use as knitted fabrics are treated with lubricants
(mineral, vegetable or ester-type oils) or waxes rather than sizes.