Page 31 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 31
Introduction 11
I00 1000
No. of installations
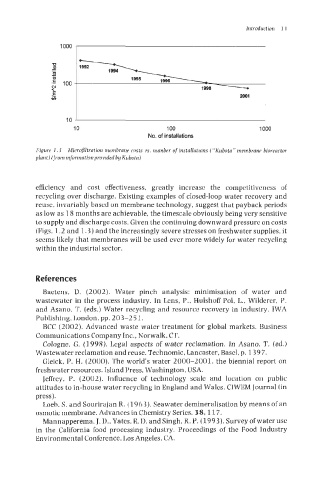
Figure I. 3 Microfiltration membrane costs 17s. number of installations (“Kubotn” rnernbrane bioreactor
plunt) (jrom information provided by Kubota)
efficiency and cost effectiveness, greatly increase the competitiveness of
recycling over discharge. Existing examples of closed-loop water recovery and
reuse, invariably based on membrane technology, suggest that payback periods
as low as 18 months are achievable, the timescale obviously being very sensitive
to supply and discharge costs. Given the continuing downward pressure on costs
(Pigs. 1.2 and 1.3) and the increasingly severe stresses on freshwater supplies, it
seems likely that membranes will be used ever more widely for water recycling
within the industrial sector.
References
Raetens, D. (2002). Water pinch analysis: minimisation of water and
wastewater in the process industry. Tn Lens, P., Hulshoff Pol, L., Wilderer, P.
and Asano, T. (eds.) Water recycling and resource recovery in industry. IWA
Publishing, London, pp. 203-2 51.
BCC (2002). Advanced waste water treatment for global markets. Business
Communications Company Inc., Norwalk, CT.
Cologne, G. (1998). Legal aspects of water reclamation. In Asano, T. (ed.)
Wastewater reclamation and reuse. Technomic, Lancaster, Basel, p. 1397.
Gleick, P. H. (2000). The world’s water 2000-2001, the biennial report on
freshwater resources. Island Press, Washington, USA.
Jeffrey, P. (2002). Influence of technology scale and location on public
attitudes to in-house water recycling in England and Wales. CTWEM Journal (in
press).
Loeb, S. and Sourirajan R. (1963). Seawater demineralisation by means of an
osmotic membrane. Advances in Chemistry Series, 38,117.
Mannapperema, J. D.. Yates, E. D. and Singh, R. P. (1993). Survey of water use
in the California food processing industry. Proceedings of the Food Industry
Environmental Conference, Los Angeles, CA.