Page 48 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 48
28 Membranesfor Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-use
Pressurized
F
'..
~
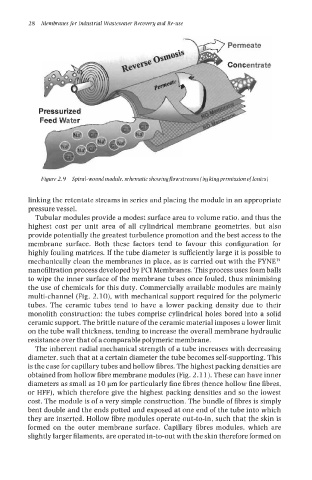
Figure 2.9 Spiral-wound module, schematic showingflow streams (by kingpermission oflonics)
linking the retentate streams in series and placing the module in an appropriate
pressure vessel.
Tubular modules provide a modest surface area to volume ratio, and thus the
highest cost per unit area of all cylindrical membrane geometries, but also
provide potentially the greatest turbulence promotion and the best access to the
membrane surface. Both these factors tend to favour this configuration for
highly fouling matrices. If the tube diameter is sufficiently large it is possible to
mechanically clean the membranes in place, as is carried out with the FYNEOZ;
nanofiltration process developed by PCI Membranes. This process uses foam balls
to wipe the inner surface of the membrane tubes once fouled, thus minimising
the use of chemicals for this duty. Commercially available modules are mainly
multi-channel (Fig. 2. lo), with mechanical support required for the polymeric
tubes. The ceramic tubes tend to have a lower packing density due to their
monolith construction: the tubes comprise cylindrical holes bored into a solid
ceramic support. The brittle nature of the ceramic material imposes a lower limit
on the tube wall thickness, tending to increase the overall membrane hydraulic
resistance over that of a comparable polymeric membrane.
The inherent radial mechanical strength of a tube increases with decreasing
diameter, such that at a certain diameter the tube becomes self-supporting. This
is the case for capillary tubes and hollow fibres. The highest packing densities are
obtained from hollow fibre membrane modules (Fig. 2.11). These can have inner
diameters as small as 10 pm for particularly fine fibres (hence hollow fine fibres,
or HFF), which therefore give the highest packing densities and so the lowest
cost. The module is of a very simple construction. The bundle of fibres is simply
bent double and the ends potted and exposed at one end of the tube into which
they are inserted. Hollow fibre modules operate out-to-in, such that the skin is
formed on the outer membrane surface. Capillary fibres modules, which are
slightly larger filaments, are operated in-to-out with the skin therefore formed on