Page 83 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 83
Membrane technology 63
where Alk represents the molar bicarbonate concentration or alkalinity. In this
equation the term pHs represents the pH at which the water is in equilibrium
with calcium carbonate, and is thus sometimes referred to as the saturation pH.
The value of (pK2 - pK,) is dependent on temperature and ionic strength.
The Langelier Saturation Index is defined as:
LSI = pH - pHs (2.38)
where pH is the actual measured pH of the water and pH, is the calculated value.
The LSI effectively measures the degree to which the water is either
supersaturated or undersaturated with calcium carbonate, and thus its
propensity for forming scale (ASTM D3 739). A negative LSI indicates a corrosive
water that will dissolve calcium carbonate scale and a positive LSI indicates a
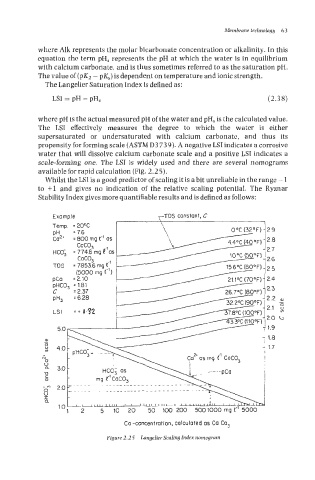
scale-forming one. The LSI is widely used and there are several nomograms
available for rapid calculation (Fig. 2.2 5).
Whilst the LSI is a good predictor of scaling it is a bit unreliable in the range -1
to +1 and gives no indication of the relative scaling potential. The Ryznar
Stability Index gives more quantifiable results and is defined as follows:
Example rTDS constant, C
pCa =2 10
Ca -concentration, calculated as Ca CO,
Figure 2.25 Langelier Scaling Index nomogram