Page 114 - Methods For Monitoring And Diagnosing The Efficiency Of Catalytic Converters A Patent - oriented Survey
P. 114
96 Methods for Monitoring and Diagnosing the Eficiency of Catalytic Converters
The method of 385179935 (1993) comprises only one aidfie1 sensor installed downstream of
a rhodium catalytic converter. The method comprises the following steps:
1) feedback-controlling the engine aidfuel ratio based on the output signal of the downstream
air/fuel sensor so as the actual aidfuel ratio corresponds to the stoichiometric one
2) detecting the inversion period of the output signal of the downstream sensor
3) judging deterioration of the catalytic converter when the inversion period detected in step 2
becomes shorter than a predefined threshold.
The method of JP6159048 (1994) also comprises only one aidfie1 sensor installed
downstream of the catalytic converter. The method comprises the following steps:
I) detecting fuel-cut of the internal combustion engine
2) making aidfie1 ratio rich when the fie1 supply is found to have been suspended for a
specified period of time
3) computing the oxygen adsorption capacity of the catalytic converter based on the detected
values of the downstream aidfuel ratio sensor and the engine intake air
4) assessing the degradation of the catalytic converter based on the computed oxygen
adsorption capacity
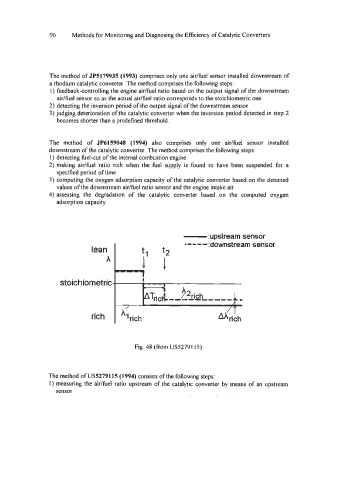
-:upstream sensor
Fig. 48 (from US52791 15)
The method of US52791 15 (1994) consists of the following steps:
1) measuring the aidfuel ratio upstream of the catalytic converter by means of an upstream
sensor