Page 46 - Methods For Monitoring And Diagnosing The Efficiency Of Catalytic Converters A Patent - oriented Survey
P. 46
28 Methods for Monitoring and Diagnosing the Eficiency of Catalytic Converters
The objective of this book is to serve as a compendium of the literature and the methods
existing in the field of monitoring of catalytic converters only, with a particular emphasis on
patent disclosures. Of course, some selected non-patent literature is also included.
The book is divided in four chapters. Each of the chapters 1 to 3 reflects a group of methods
for the monitoring of catalytic converters.
Chapter 1 comprises methods that use oxygen or airlfuel ratio (A or lambda) sensors upstream
and downstream of the converter in order to detect degradation of the converter.
Chapter 2 comprises methods that use temperature measurements of the exhaust gases inside
or outside the catalytic converter in order to detect degradation of the converter.
Chapter 3 comprises all other methods not covered by the methods of chapters 1 and 2. Mostly
this chapter comprises direct methods of diagnosis of catalytic converters by means of HC, CO
or NO, sensors.
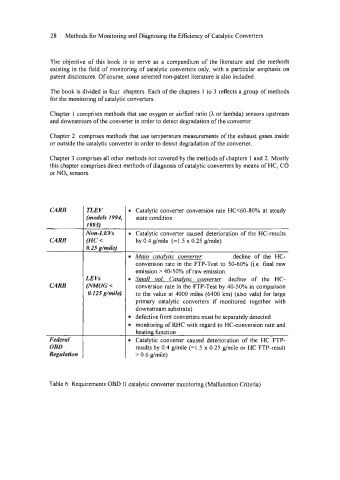
CARB TI,EV Catalytic converter conversion rate HC<60-80% at steady
(models 1994, state condition
1995)
Non-I, E Kv Catalytic converter caused deterioration of the HC-results
CARB (HC by 0.4 g/mile (=IS x 0.25 g/mile)
0.2 5 g/inile)
~~
Main cataZvfic converfer: decline of the HC-
conversion rate in the FTP-Test to SO-60% (i.e. final raw
emission > 40-50% of raw emission
LEVs Snrall vol. Catalytic com)erter: decline of the HC-
CARB (NMOG conversion rate in the FTP-Test by 4040% in comparison
0.125 g/mile) to the value at 4000 miles (6400 km) (also valid for large
primary catalytic converters if monitored together with
downstream substrate)
defective front converters must be separately detected
monitoring of RHC with regard to HC-conversion rate and
heating function
Federal Catalytic converter caused deterioration of the HC FTP-
OBD results by 0.4 @mile (=I .5 x 0.25 g/mile or HC FTP-result
Regulation > 0.6 g/mile)
Table 6: Requirements OBD I I catalytic converter monitoring (Malfunction Criteria)