Page 90 - Methods For Monitoring And Diagnosing The Efficiency Of Catalytic Converters A Patent - oriented Survey
P. 90
72 Methods for Monitoring and Diagnosing the Efficiency of Catalytic Converters
In US5265416 (1993) the aidfuel ratio fed to the engine is perturbed on a cylinder-to-cylinder
basis above and below a mean or average aidfuel ratio. That is, individual cylinders are fed, in
their firing sequence, alternately rich and lean aidfuel mixtures with no overall rich or lean shift
of the fuel mixture (maldistribution). The output signal of the downstream of the catalytic
converter installed EGO sensor during the perturbation is compared to the corresponding
signal measured a time period either immediately preceding or immediately following this
perturbation. As it can be seen from fig. 34a, the EGO sensor output is substantially unaffected
for both cases of perturbed and non-perturbed engine aidfuel ratio and for the case of an
efficient catalytic converter. The EGO sensor output is measurably affected by cylinder-to-
cylinder maldistribution in the case of low efficiency converter (fig. 34b). In both figures the
EGO sensor output is shown as the portion of time the output signal is on the rich side of the
EGO sensor switch-point. The difference of the EGO outputs for the cases of cylinder-to-
cylinder aidfuel ratio maldistribution and non-maldistribution is a measure of catalytic
converter efficiency.
airffiel t
ratio ' I lean perturbation
time
Fig. 35 (from US5272872)
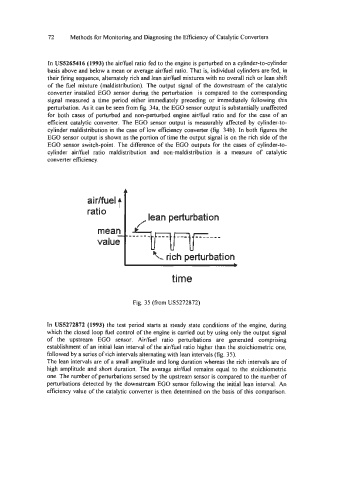
In US5272872 (1993) the test period starts at steady state conditions of the engine, during
which the closed loop fuel control of the engine is carried out by using only the output signal
of the upstream EGO sensor. Aidfuel ratio perturbations are generated comprising
establishment of an initial lean interval of the aidfuel ratio higher than the stoichiometric one,
followed by a series of rich intervals alternating with lean intervals (fig. 35).
The lean intervals are of a small amplitude and long duration whereas the rich intervals are of
high amplitude and short duration. The average aidfuel remains equal to the stoichiometric
one. The number of perturbations sensed by the upstream sensor is compared to the number of
perturbations detected by the downstream EGO sensor following the initial lean interval. An
efficiency value of the catalytic converter is then determined on the basis of this comparison.