Page 178 - A Practical Guide from Design Planning to Manufacturing
P. 178
Microarchitecture 151
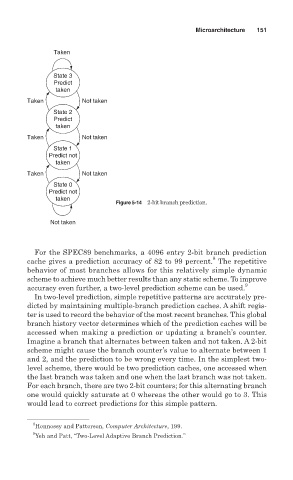
Taken
State 3
Predict
taken
Taken Not taken
State 2
Predict
taken
Taken Not taken
State 1
Predict not
taken
Taken Not taken
State 0
Predict not
taken
Figure 5-14 2-bit branch prediction.
Not taken
For the SPEC89 benchmarks, a 4096 entry 2-bit branch prediction
8
cache gives a prediction accuracy of 82 to 99 percent. The repetitive
behavior of most branches allows for this relatively simple dynamic
scheme to achieve much better results than any static scheme. To improve
accuracy even further, a two-level prediction scheme can be used. 9
In two-level prediction, simple repetitive patterns are accurately pre-
dicted by maintaining multiple-branch prediction caches. A shift regis-
ter is used to record the behavior of the most recent branches. This global
branch history vector determines which of the prediction caches will be
accessed when making a prediction or updating a branch’s counter.
Imagine a branch that alternates between taken and not taken. A 2-bit
scheme might cause the branch counter’s value to alternate between 1
and 2, and the prediction to be wrong every time. In the simplest two-
level scheme, there would be two prediction caches, one accessed when
the last branch was taken and one when the last branch was not taken.
For each branch, there are two 2-bit counters; for this alternating branch
one would quickly saturate at 0 whereas the other would go to 3. This
would lead to correct predictions for this simple pattern.
8
Hennessy and Patterson, Computer Architecture, 199.
9
Yeh and Patt, “Two-Level Adaptive Branch Prediction.”