Page 183 - A Practical Guide from Design Planning to Manufacturing
P. 183
156 Chapter Five
has the job of starting the operating system. The operating system (OS)
then loads applications for the user. Once running, the application runs
by sending macroinstructions to the microprocessor for execution. The
instructions can send specific requests for service to the operating
system by calling device drivers. The OS will in turn execute its own rou-
tines on the processor or call device drivers stored in the BIOS.
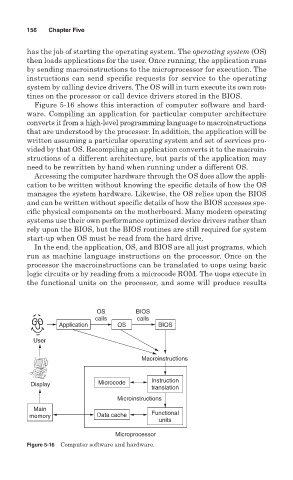
Figure 5-16 shows this interaction of computer software and hard-
ware. Compiling an application for particular computer architecture
converts it from a high-level programming language to macroinstructions
that are understood by the processor. In addition, the application will be
written assuming a particular operating system and set of services pro-
vided by that OS. Recompiling an application converts it to the macroin-
structions of a different architecture, but parts of the application may
need to be rewritten by hand when running under a different OS.
Accessing the computer hardware through the OS does allow the appli-
cation to be written without knowing the specific details of how the OS
manages the system hardware. Likewise, the OS relies upon the BIOS
and can be written without specific details of how the BIOS accesses spe-
cific physical components on the motherboard. Many modern operating
systems use their own performance optimized device drivers rather than
rely upon the BIOS, but the BIOS routines are still required for system
start-up when OS must be read from the hard drive.
In the end, the application, OS, and BIOS are all just programs, which
run as machine language instructions on the processor. Once on the
processor the macroinstructions can be translated to uops using basic
logic circuits or by reading from a microcode ROM. The uops execute in
the functional units on the processor, and some will produce results
OS BIOS
calls calls
Application OS BIOS
User
Macroinstructions
Display Microcode Instruction
translation
Microinstructions
Main
memory Data cache Functional
units
Microprocessor
Figure 5-16 Computer software and hardware.