Page 67 - A Practical Guide from Design Planning to Manufacturing
P. 67
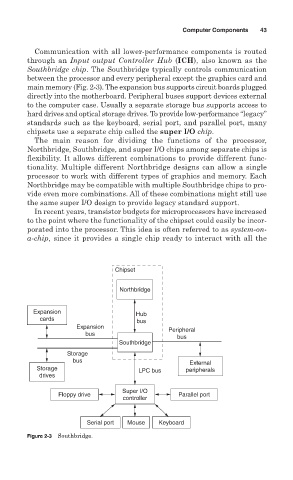
Computer Components 43
Communication with all lower-performance components is routed
through an Input output Controller Hub (ICH), also known as the
Southbridge chip. The Southbridge typically controls communication
between the processor and every peripheral except the graphics card and
main memory (Fig. 2-3). The expansion bus supports circuit boards plugged
directly into the motherboard. Peripheral buses support devices external
to the computer case. Usually a separate storage bus supports access to
hard drives and optical storage drives. To provide low-performance “legacy”
standards such as the keyboard, serial port, and parallel port, many
chipsets use a separate chip called the super I/O chip.
The main reason for dividing the functions of the processor,
Northbridge, Southbridge, and super I/O chips among separate chips is
flexibility. It allows different combinations to provide different func-
tionality. Multiple different Northbridge designs can allow a single
processor to work with different types of graphics and memory. Each
Northbridge may be compatible with multiple Southbridge chips to pro-
vide even more combinations. All of these combinations might still use
the same super I/O design to provide legacy standard support.
In recent years, transistor budgets for microprocessors have increased
to the point where the functionality of the chipset could easily be incor-
porated into the processor. This idea is often referred to as system-on-
a-chip, since it provides a single chip ready to interact with all the
Chipset
Northbridge
Expansion Hub
cards
bus
Expansion Peripheral
bus
bus
Southbridge
Storage
bus External
Storage LPC bus peripherals
drives
Super I/O
Floppy drive Parallel port
controller
Serial port Mouse Keyboard
Figure 2-3 Southbridge.