Page 255 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 255
THERMAL SENSORS 235
10
« 5 --
18
1.0xl0 /cm 3 x -^
19
..-••'"l.5xl0 /cm' 3
—I 1 1
100 200 300
Temperature (K)
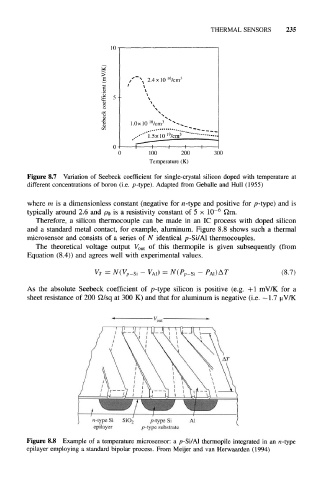
Figure 8.7 Variation of Seebeck coefficient for single-crystal silicon doped with temperature at
different concentrations of boron (i.e. p-type). Adapted from Geballe and Hull (1955)
where m is a dimensionless constant (negative for n-type and positive for p-type) and is
-6
typically around 2.6 and p 0 is a resistivity constant of 5 x 10 £2m.
Therefore, a silicon thermocouple can be made in an IC process with doped silicon
and a standard metal contact, for example, aluminum. Figure 8.8 shows such a thermal
microsensor and consists of a series of N identical p-Si/Al thermocouples.
The theoretical voltage output V out of this thermopile is given subsequently (from
Equation (8.4)) and agrees well with experimental values.
- - (8.7)
V T = N(V p. Si V M) = N(P p. Si
As the absolute Seebeck coefficient of p-type silicon is positive (e.g. +1 mV/K for a
sheet resistance of 200 fi/sq at 300 K) and that for aluminum is negative (i.e. —1.7 uV/K
-type substrate
Figure 8.8 Example of a temperature microsensor: a p-Si/Al thermopile integrated in an n-type
epilayer employing a standard bipolar process. From Meijer and van Herwaarden (1994)