Page 259 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 259
THERMAL SENSORS 239
8.2.4 SAW Temperature Sensor
In certain circumstances, it may be cost-effective to use other technologies. For example,
the remote wireless sensing of temperature - perhaps on a rotating part - requires a
temperature IC, radio frequency (RF) transmitter, and a battery power supply. An alter-
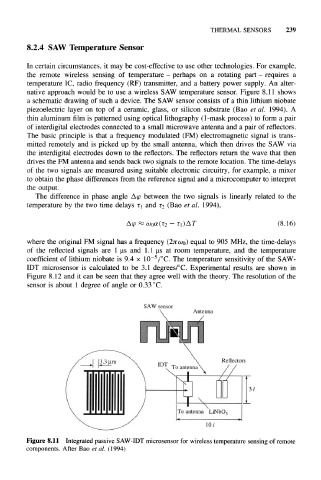
native approach would be to use a wireless SAW temperature sensor. Figure 8.11 shows
a schematic drawing of such a device. The SAW sensor consists of a thin lithium niobate
piezoelectric layer on top of a ceramic, glass, or silicon substrate (Bao et al. 1994). A
thin aluminum film is patterned using optical lithography (1-mask process) to form a pair
of interdigital electrodes connected to a small microwave antenna and a pair of reflectors.
The basic principle is that a frequency modulated (FM) electromagnetic signal is trans-
mitted remotely and is picked up by the small antenna, which then drives the SAW via
the interdigital electrodes down to the reflectors. The reflectors return the wave that then
drives the FM antenna and sends back two signals to the remote location. The time-delays
of the two signals are measured using suitable electronic circuitry, for example, a mixer
to obtain the phase differences from the reference signal and a microcomputer to interpret
the output.
The difference in phase angle A<p between the two signals is linearly related to the
temperature by the two time delays T\ and 12 (Bao et al. 1994),
(8.16)
where the original FM signal has a frequency (ITCCDQ] equal to 905 MHz, the time-delays
of the reflected signals are 1 us and 1.1 us at room temperature, and the temperature
-5
coefficient of lithium niobate is 9.4 x 10 /°C. The temperature sensitivity of the SAW-
IDT microsensor is calculated to be 3.1 degrees/°C. Experimental results are shown in
Figure 8.12 and it can be seen that they agree well with the theory. The resolution of the
sensor is about 1 degree of angle or 0.33 °C.
SAW sensor
Antenna
10/
Figure 8.11 Integrated passive SAW-IDT microsensor for wireless temperature sensing of remote
components. After Bao et al. (1994)