Page 261 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 261
RADIATION SENSORS 241
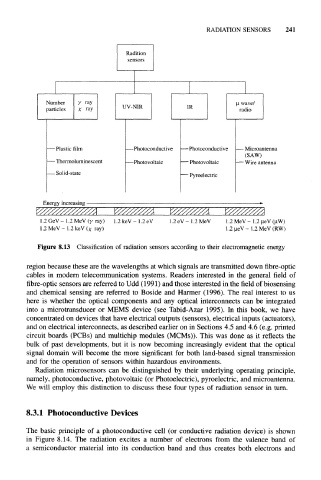
Radition
sensors
Number X ray
particles X ray
- Plastic film -Photoconductive -Photoconductive - Microantenna
(SAW)
- Thermoluminescent -Photovoltaic - Photovoltaic — Wire antenna
- Solid-state " Pyroelectric
Energy increasing
L.2GeV-1.2MeV(x ray) 1.2keV-1.2eV 1.2eV-1.2MeV 1.2MeV- 1.2
1.2MeV- 1.2keV(;r ray) 1.2jieV-1.2MeV(RW)
Figure 8.13 Classification of radiation sensors according to their electromagnetic energy
region because these are the wavelengths at which signals are transmitted down fibre-optic
cables in modern telecommunication systems. Readers interested in the general field of
fibre-optic sensors are referred to Udd (1991) and those interested in the field of biosensing
and chemical sensing are referred to Boside and Harmer (1996). The real interest to us
here is whether the optical components and any optical interconnects can be integrated
into a microtransducer or MEMS device (see Tabid-Azar 1995). In this book, we have
concentrated on devices that have electrical outputs (sensors), electrical inputs (actuators),
and on electrical interconnects, as described earlier on in Sections 4.5 and 4.6 (e.g. printed
circuit boards (PCBs) and multichip modules (MCMs)). This was done as it reflects the
bulk of past developments, but it is now becoming increasingly evident that the optical
signal domain will become the more significant for both land-based signal transmission
and for the operation of sensors within hazardous environments.
Radiation microsensors can be distinguished by their underlying operating principle,
namely, photoconductive, photovoltaic (or Photoelectric), pyroelectric, and microantenna.
We will employ this distinction to discuss these four types of radiation sensor in turn.
8.3.1 Photoconductive Devices
The basic principle of a photoconductive cell (or conductive radiation device) is shown
in Figure 8.14. The radiation excites a number of electrons from the valence band of
a semiconductor material into its conduction band and thus creates both electrons and