Page 49 - MODELING OF ASPHALT CONCRETE
P. 49
Modeling of Asphalt Binder Rheology and Its Application to Modified Binders 27
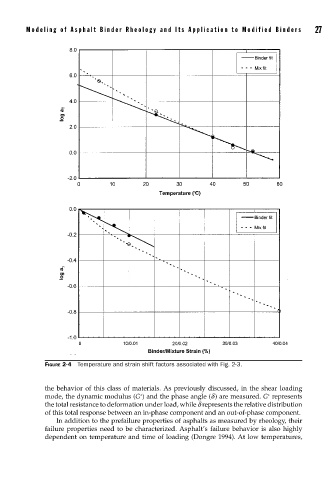
FIGURE 2-4 Temperature and strain shift factors associated with Fig. 2-3.
the behavior of this class of materials. As previously discussed, in the shear loading
∗
∗
mode, the dynamic modulus (G ) and the phase angle (d) are measured. G represents
the total resistance to deformation under load, while d represents the relative distribution
of this total response between an in-phase component and an out-of-phase component.
In addition to the prefailure properties of asphalts as measured by rheology, their
failure properties need to be characterized. Asphalt’s failure behavior is also highly
dependent on temperature and time of loading (Dongre 1994). At low temperatures,