Page 107 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 107
Thermodynamics of Chemical Reactions 77
where C is in cal/mol K or J/mol K and T is in degrees Kelvin
p i
(1 cal = 4.184 J).
If stoichiometric quantities of the reactants enter and the products
leave at the same temperature as represented by the equation:
α A + α B → α C + α D (2-95)
2
3
1
4
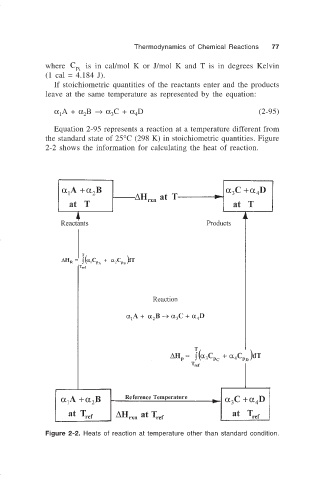
Equation 2-95 represents a reaction at a temperature different from
the standard state of 25°C (298 K) in stoichiometric quantities. Figure
2-2 shows the information for calculating the heat of reaction.
Figure 2-2. Heats of reaction at temperature other than standard condition.