Page 116 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 116
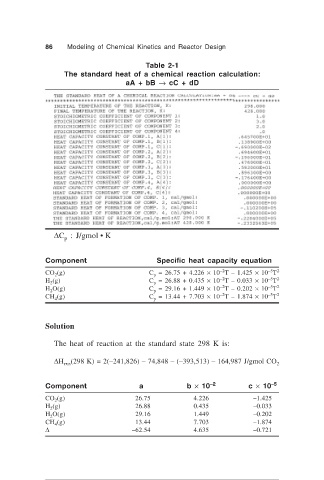
86 Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
Table 2-1
The standard heat of a chemical reaction calculation:
aA + bB → cC + dD
∆C : J/gmol • K
p
Component Specific heat capacity equation
–5 2
–2
CO (g) C = 26.75 + 4.226 × 10 T – 1.425 × 10 T
2
p
–5 2
–2
H (g) C = 26.88 + 0.435 × 10 T – 0.033 × 10 T
2
p
–2
–5 2
H O(g) C = 29.16 + 1.449 × 10 T – 0.202 × 10 T
2
p
–5 2
–2
CH (g) C = 13.44 + 7.703 × 10 T – 1.874 × 10 T
p
4
Solution
The heat of reaction at the standard state 298 K is:
∆H (298 K) = 2(–241,826) – 74,848 – (–393,513) – 164,987 J/gmol CO 2
rxn
Component a b × 10 –2 c × 10 –5
CO (g) 26.75 4.226 –1.425
2
H (g) 26.88 0.435 –0.033
2
H O(g) 29.16 1.449 –0.202
2
CH (g) 13.44 7.703 –1.874
4
∆ –62.54 4.635 –0.721