Page 135 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 135
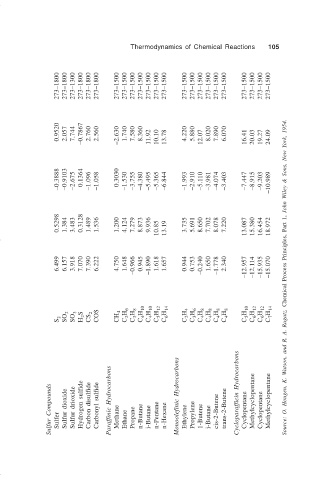
Thermodynamics of Chemical Reactions 105
273–1800 273–1800 273–1300 273–1800 273–1800 273–1800 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500
0.9520 2.057 7.744 –0.7867 2.760 2.560 –2.630 1.740 7.580 8.360 11.92 10.10 13.78 4.220 5.880 12.07 8.020 7.890 6.070 16.41 20.03 19.27 24.09
–0.3888 –0.9103 –2.675 0.1364 –1.096 –1.058 0.3030 –1.530 –3.755 –4.380 –5.495 –5.365 –6.844 –1.993 –2.910 –5.110 –3.981 –4.074 –3.403 –7.447 –8.915 –9.203 –10.989
0.5298 1.384 3.483 0.3128 1.489 1.536 1.200 4.124 7.279 8.873 9.936 10.85 13.19 3.735 5.691 8.650 7.702 8.078 7.220 13.087 15.380 16.454 18.972
6.499 6.157 3.918 7.070 7.390 6.222 4.750 1.648 –0.966 0.945 –1.890 1.618 1.657 0.944 0.753 –0.240 1.650 –1.778 2.340 –12.957 –12.114 –15.935 –15.070 Source: O. Hougen, K. Watson, and R. A. Ragatz, Chemical Process Principles, Part 1, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1954.
S 2 SO 2 SO 3 H 2 S CS 2 COS CH 4 C 2 H 6 C 3 H 8 C 4 H 10 C 4 H 10 C 5 H 12 C 6 H 14 C 2 H 4 C 3 H 6 C 4 H 8 C 4 H 8 C 4 H 8 C 4 H 8 C 5 H 10 C 6 H 12 C 6 H 12 C 7 H 14
Sulfur Compounds Sulfer Sulfur dioxide Sulfur drioxide Hydrogen sulfide Carbon disulfide Carbonyl sulfide Paraffinic Hydrocarbons Methane Ethane Propane n-Butane i-Butane n-Pentane n-Hexane Monoolefinic Hydrocarbons Ethylene Propylene 1-Butene i-Butane cis-2-Butene trans-2-Butene Cycloparafficin Hydrocarbons Cyclopentane Methylcyclopentane Cyclopentane Methylcyclopentane