Page 138 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 138
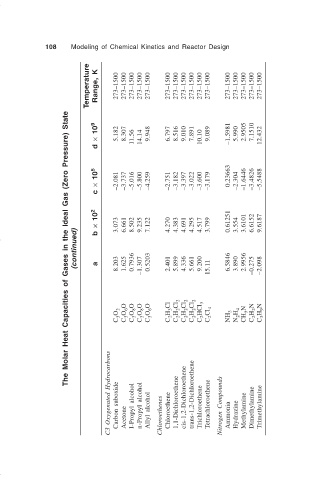
108 Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
Temperature Range, K 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500
The Molar Heat Capacities of Gases in the Ideal Gas (Zero Pressure) State
d × 10 9 5.182 8.307 11.56 14.14 9.948 6.797 8.516 9.010 7.891 10.10 9.089 –1.5981 5.990 2.9505 7.1510 12.432
c × 10 5 –2.081 –3.737 –5.016 –5.800 –4.259 –2.751 –3.182 –3.397 –3.022 –3.600 –3.179 0.23663 –2.304 –1.6446 –3.4826 –5.5488
× 10 2 3.073 6.661 8.502 9.235 7.122 4.270 4.383 4.691 4.295 4.517 3.799 0.61251 3.554 3.6101 6.6152 9.6187
(continued) b a 8.203 1.625 0.7936 –1.307 0.5203 2.401 5.899 4.336 5.661 9.200 15.11 6.5846 3.890 2.9956 –0.275 –2.098
C 3 O 2 O C 3 O 6 O C 3 O 8 O C 3 O 8 O C 3 O 6 C 2 H 3 Cl C 2 H 2 Cl 2 C 2 H 2 Cl 2 C 2 H 2 Cl 2 C 2 HCl 3 C 2 Cl 4 NH 3 N 2 H 4 CH 5 N C 2 H 2 N C 3 H 9 N
C3 Oxygenated Hydrocarbons Carbon suboxide Acetone I-Propyl alcohol n-Propyl alcohol Allyl alcohol Chloroethenes Chloroethene 1,1-Dichloroethene cis-1,2-Dichloroethene trans-1,2-Dichloroethene Trichloroethene Tetrachloroethene Nitrogen Compounds Ammonia Hydrazine Methylamine Dimethylamine Trimethylamine