Page 143 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 143
Reaction Rate Expression 113
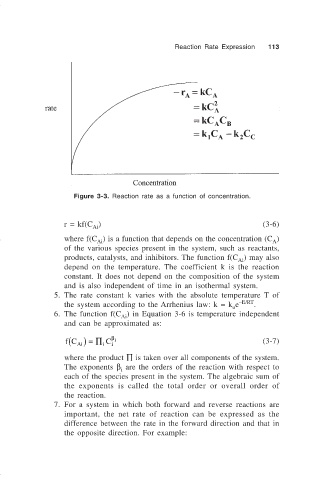
Figure 3-3. Reaction rate as a function of concentration.
r = kf(C ) (3-6)
Ai
where f(C ) is a function that depends on the concentration (C )
Ai
A
of the various species present in the system, such as reactants,
products, catalysts, and inhibitors. The function f(C ) may also
Ai
depend on the temperature. The coefficient k is the reaction
constant. It does not depend on the composition of the system
and is also independent of time in an isothermal system.
5. The rate constant k varies with the absolute temperature T of
the system according to the Arrhenius law: k = k e –E/RT .
o
6. The function f(C ) in Equation 3-6 is temperature independent
Ai
and can be approximated as:
fC ( Ai ) =∏ i C i i β (3-7)
where the product ∏ is taken over all components of the system.
The exponents β are the orders of the reaction with respect to
i
each of the species present in the system. The algebraic sum of
the exponents is called the total order or overall order of
the reaction.
7. For a system in which both forward and reverse reactions are
important, the net rate of reaction can be expressed as the
difference between the rate in the forward direction and that in
the opposite direction. For example: