Page 141 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 141
Reaction Rate Expression 111
(–r ) = f{temperature, concentration} (3-4)
A
The Swedish chemist Arrhenius first suggested that the temperature
dependence of the specific reaction rate k could be correlated by an
equation of the type k(T) = k e –E/RT . Therefore,
o
a
(–r ) = kC = k e –E/RT a A
C
o
A
A
where E = activation energy (J/mol)
k = frequency factor
o
a = reaction order
C = concentration of reactant A
A
T = absolute temperature, K
R = gas constant = 1.987 cal/mol • K = 8.314 J/mol •K
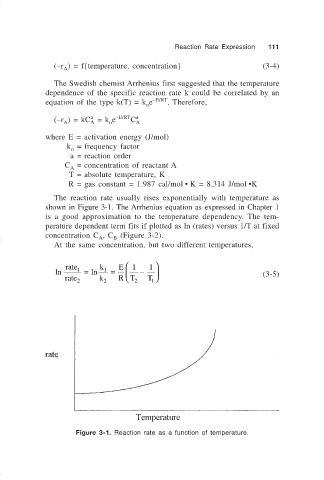
The reaction rate usually rises exponentially with temperature as
shown in Figure 3-1. The Arrhenius equation as expressed in Chapter 1
is a good approximation to the temperature dependency. The tem-
perature dependent term fits if plotted as ln (rates) versus 1/T at fixed
concentration C , C (Figure 3-2).
A
B
At the same concentration, but two different temperatures,
rate k E 1 1
ln 1 = ln 1 = − (3-5)
rate 2 k 2 RT 2 T
1
Figure 3-1. Reaction rate as a function of temperature.