Page 136 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 136
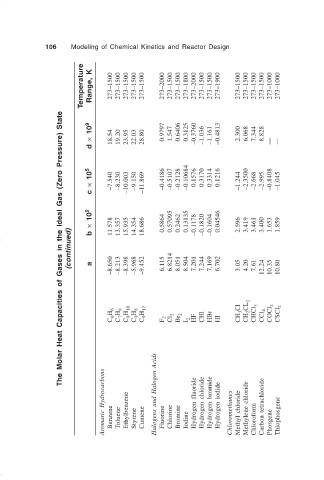
106 Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
Temperature Range, K 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–2000 273–1500 273–1500 273–1800 273–2000 273–1500 273–1500 273–1900 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1500 273–1000 273–1000
The Molar Heat Capacities of Gases in the Ideal Gas (Zero Pressure) State
d × 10 9 18.54 19.20 23.95 22.03 28.80 0.9797 1.547 0.6406 0.3125 –0.3760 –1.036 –1.161 –0.4813 2.300 6.068 7.344 8.828 — —
c × 10 5 –7.540 –8.230 –10.003 –9.150 –11.869 –0.4186 –0.5107 –0.2128 –0.10684 0.1576 0.3170 0.3314 0.1216 –1.244 –2.3500 –2.668 –2.995 –0.8408 –1.045
× 10 2 11.578 13.357 15.935 14.354 18.686 0.5864 0.57095 0.2462 0.13135 –0.1178 –0.1820 –0.1604 0.04546 2.596 3.419 3.461 3.400 1.653 1.859
(continued) b a –8.650 –8.213 –8.398 –5.968 –9.452 6.115 6.8214 8.051 8.504 7.201 7.244 7.169 6.702 3.05 4.20 7.61 12.24 10.35 10.80
C 6 H 6 C 7 H 8 C 8 H 10 C 8 H 8 C 9 H 12 F 2 Cl 2 Br 2 I 2 HF CHl HBr HI CH 3 Cl CH 2 CL 2 CHCl 3 CCl 4 COCl 2 CSCl 2
Aromatic Hydrocarbons Benzene Toluene Ethylbenzene Styrene Cumene Halogens and Halogen Acids Fluorine Chlorine Bromine Iodine Hydrogen fluoride Hydrogen chloride Hydrogen bromide Hydrogen iodide Chloromethanes Methyl chloride Methylene chloride Chloroform Carbon tetrachloride Phosgene Thiophosgene