Page 142 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 142
112 Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
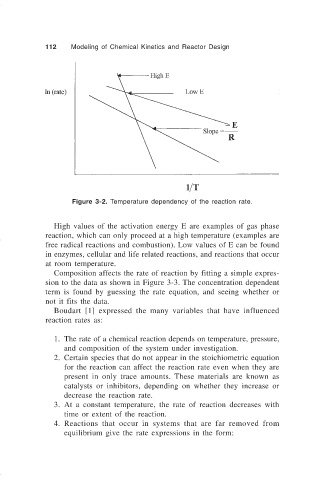
Figure 3-2. Temperature dependency of the reaction rate.
High values of the activation energy E are examples of gas phase
reaction, which can only proceed at a high temperature (examples are
free radical reactions and combustion). Low values of E can be found
in enzymes, cellular and life related reactions, and reactions that occur
at room temperature.
Composition affects the rate of reaction by fitting a simple expres-
sion to the data as shown in Figure 3-3. The concentration dependent
term is found by guessing the rate equation, and seeing whether or
not it fits the data.
Boudart [1] expressed the many variables that have influenced
reaction rates as:
1. The rate of a chemical reaction depends on temperature, pressure,
and composition of the system under investigation.
2. Certain species that do not appear in the stoichiometric equation
for the reaction can affect the reaction rate even when they are
present in only trace amounts. These materials are known as
catalysts or inhibitors, depending on whether they increase or
decrease the reaction rate.
3. At a constant temperature, the rate of reaction decreases with
time or extent of the reaction.
4. Reactions that occur in systems that are far removed from
equilibrium give the rate expressions in the form: