Page 33 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 33
Reaction Mechanisms and Rate Expressions 3
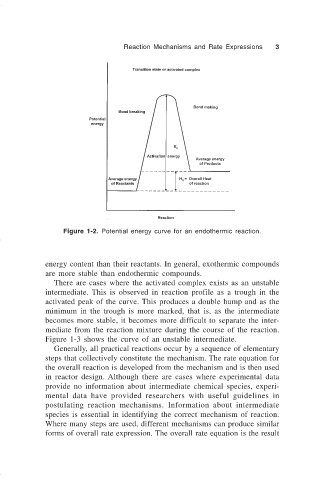
Figure 1-2. Potential energy curve for an endothermic reaction.
energy content than their reactants. In general, exothermic compounds
are more stable than endothermic compounds.
There are cases where the activated complex exists as an unstable
intermediate. This is observed in reaction profile as a trough in the
activated peak of the curve. This produces a double hump and as the
minimum in the trough is more marked, that is, as the intermediate
becomes more stable, it becomes more difficult to separate the inter-
mediate from the reaction mixture during the course of the reaction.
Figure 1-3 shows the curve of an unstable intermediate.
Generally, all practical reactions occur by a sequence of elementary
steps that collectively constitute the mechanism. The rate equation for
the overall reaction is developed from the mechanism and is then used
in reactor design. Although there are cases where experimental data
provide no information about intermediate chemical species, experi-
mental data have provided researchers with useful guidelines in
postulating reaction mechanisms. Information about intermediate
species is essential in identifying the correct mechanism of reaction.
Where many steps are used, different mechanisms can produce similar
forms of overall rate expression. The overall rate equation is the result