Page 57 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 57
Reaction Mechanisms and Rate Expressions 27
CHO CO ⋅
O 6 H 12 C 6 OH R 2 2 ⋅ CH 2 OH⋅ CH 32 ) 2( OH R 2 O H 2 XH 2
Equation of reaction + HO 6 C 6 = O H 2 12 CHO + R 1 ⋅ = O H 2 + CH 2 = O H 2 CHO + = CH 32 ) OH)( C( ⋅ COOH + R 1 ⋅ = O H 2 + CHO + CH 3 ⋅ = 2 O H 2 O + N 2 COCHX + ⋅ R⋅ = X 2 +
CH 22 + O 11 12 OR 2 ) CH( R 1 2 CH⋅ CH 2 : CH 2 CO⋅ CH 3 COOR 2 R 1 ⋅ OH) CH( CH 3 ⋅ = NO 2 NH 2 COCH 3 ⋅ R⋅
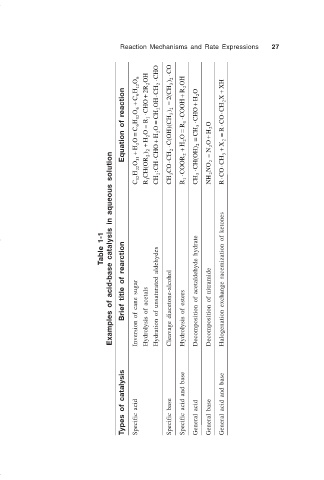
Table 1-1 Examples of acid-base catalysis in aqueous solution
Brief title of rearction Inversion of cane sugar Hydrolysis of acetals Hydration of unsaturated aldehydes Cleavage diacetone-alcohol Hydrolysis of esters Decomposition of acetaldehyde hydrate Decomposition of nitramide Halogenation exchange racemization of ketones
Types of catalysis Specific acid Specific base Specific acid and base General acid General base General acid and base