Page 59 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 59
Reaction Mechanisms and Rate Expressions 29
gases up to the catalyst surface, diffusion of reactants into the interior
of the pellet, diffusion of the products back to the exterior surface,
and finally the transfer of the products from the exterior surface to
the main stream. Interpreting the experimental results requires minimizing
the resistance offered by each of these physical processes and focusing
on the chemical aspects of the reaction. The chemical procedures
involve activated adsorption of reactants with or without dissociation,
surface reactions on active sites, and activated desorption of the
products. The uncatalyzed reaction also takes place in the main gas
stream simultaneously with the surface reaction.
In industrial applications of kinetics, an understanding of the
mechanisms of chemical reactions is essential. This is helpful in
establishing the optimum operating conditions in relation to parameters
such as temperature, pressure, feed composition, space velocity, and
the extent of recycling and conversion. Yang and Hougen [7] have
established procedures in planning and correlating experimental data
for gaseous reactions catalyzed by solids. They provided methods for
eliminating, minimizing, or evaluating the temperatures and con-
centration gradients in gas films and catalyst pellets. Hougen and
Watson [8] have developed rate equations for various mechanisms that
may occur in gaseous reactions when catalyzed by solid surfaces. The
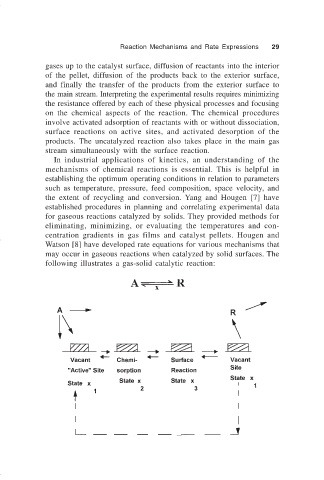
following illustrates a gas-solid catalytic reaction: