Page 418 - Modelling in Transport Phenomena A Conceptual Approach
P. 418
398 CHAPTER 9. STEADY MICROSCOPIC BALANCES WITH GEN.
9.5.2 Diffusion Into a Falling Liquid Film
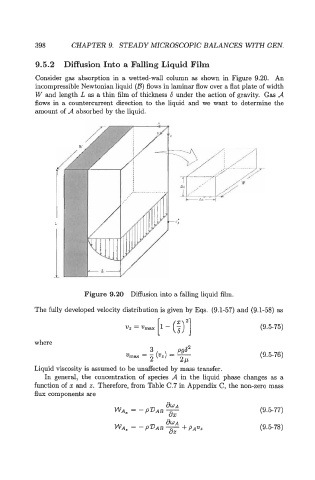
Consider gas absorption in a wetted-wall column as shown in Figure 9.20. An
incompressible Newtonian liquid (a) flows in laminar flow over a flat plate of width
W and length L as a thin film of thickness 6 under the action of gravity. Gas A
flows in a countercurrent direction to the liquid and we want to determine the
amount of A absorbed by the liquid.
Figure 9.20 Diffusion into a falling liquid film.
The fully developed velocity distribution is given by Eqs. (9.1-57) and (9.1-58) as
(9.575)
where
3
Pd2
v,, = 5 (VI) = - (9.576)
2P
Liquid viscosity is assumed to be unaffected by mass transfer.
In general, the concentration of species A in the liquid phase changes as a
function of 2 and x. Therefore, from Table C.7 in Appendix C, the non-zero mass
flux components are
(9.577)
(9.578)