Page 537 - Modelling in Transport Phenomena A Conceptual Approach
P. 537
A.8. METHODS OF INTEGRATION 517
T ClJ
( K) ( cal/ mol. K)
300 19.65
400 26.74
500 32.80
600 37.74
700 41.75
800 45.06
900 47.83
1000 50.16
Solution
The amount of heat necessary to increase the temperature of benzene vapor from
300K to 1OOOK under coastant pressure is calculated from the formula
Q=A& 11; cp dT
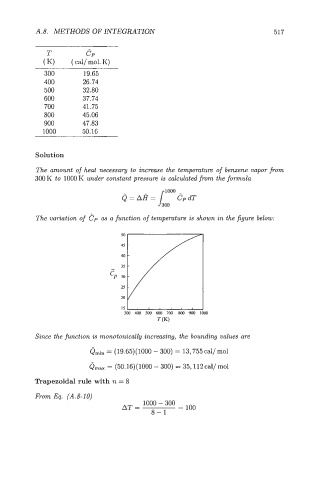
The variation of Cp as a function of temperature is shown in the figure below:
Since the function is monotonically increasing, the bounding values are
-
Qmin = (19.65)(1000 - 300) = 13,755 tal/ mol
.,
Qmax = (50.16)(1000 - 300) = 35,112cal/ mol
Trapezoidal rule with n = 8
From Eq. (A.8-10)
1000 - 300 =
AT =
8-1