Page 30 - MODERN ASPECTS OF ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 30
Voltaic Cells in Electrochemistry and Surface ChemistryAof Liquids
. 17
.
while a dashed vertical bar ( . ) represents a junction between liquids. A
..
. .
double, dashed vertical bar (. . ) represents a liquid junction in which the
diffusion potential has been assumed to be eliminated.
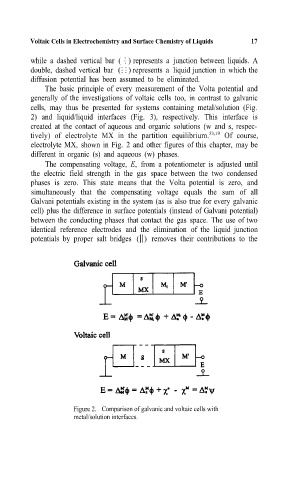
The basic principle of everymeasurement of the Volta potential and
generally of the investigations of voltaic cells too, in contrast to galvanic
cells, may thus be presented for systems containing metal/solution (Fig.
2) and liquid/liquid interfaces (Fig. 3), respectively. This interface is
created at the contact of aqueous and organic solutions (w and s, respec-
tively) of electrolyte MX in the partition equilibrium. 53,19 Of course,
electrolyte MX, shown in Fig. 2 and other figures of this chapter, may be
different in organic (s) and aqueous (w) phases.=
The compensating voltage, E, from a potentiometer is adjusted until
the electric field strength in the gas space between the two condensed
phases is zero. This state means that the Volta potential is zero, and
simultaneously that the compensating voltage equals the sum of all
Galvani potentials existing in the system (as is also true for every galvanic
cell) plus the difference in surface potentials (instead of Galvani potential)
between the conducting phases that contact the gas space.= The use of two
identical reference electrodes and the elimination of the liquid junction
potentials byproper salt bridges () removes their contributions to the
Figure 2. Comparison of galvanic and voltaic cells with
metal/solution interfaces.=