Page 34 - MODERN ASPECTS OF ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 34
Voltaic Cells in Electrochemistry and Surface Chemistry of LiquidsA
21
impedance electrometric device. 4–17,28–30 Usually gold foil coated with an
alpha emitter (e.g., 241 Am) is used as the mediating air electrode. It ionizes
the air gap between the air electrode and liquid surface so that a small
current (a few picoamperes) can flow. The ionization of the gas, which is
due to radiation, allows the direct compensation and measurement of the
voltage of the investigated system. Modern experimental arrangements
are presented in Refs. 28-29.The simultaneous use of two ionizing probes
placed above the investigated and reference surfaces m¸es possible the
w 29-30
direct differential measurement of ∆χ .
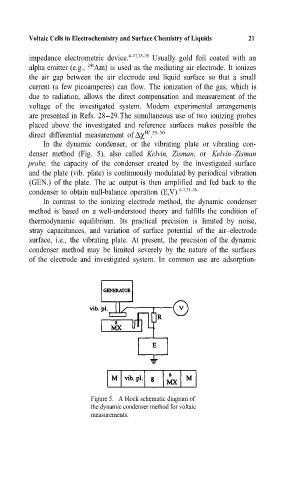
In the dynamic condenser, or the vibrating plate or vibrating con-
denser method (Fig. 5), also called Kelvin, Zisman, or Kelvin–Zisman
probe, the capacityof the condenser created bythe investigated surface
and the plate (vib.= plate) is continuously modulated by periodical vibration
(GEN.) of the plate. The ac output is then amplified and fed back to the
condenser to obtain null-balance operation (E,V). 4–7,31–36
In contrast to the ionizing electrode method, the dynamic condenser
method is based on a well-understood theoryand fulfills the condition of
thermodynamic equilibrium.= Its practical precision is limited by noise,
stray capacitances, and variation of surface potential of the air–electrode
surface, i.e.,= the vibrating plate.= At present, the precision of the dynamic
condenser method may be limited severely by the nature of the surfaces
of the electrode and investigated system.= In common use are adsorption -
Figure 5. A block schematic diagram of
the dynamic condenser method for voltaic
measurements.