Page 38 - MODERN ASPECTS OF ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 38
Voltaic Cells in Electrochemistry and Surface Chemistry of Liquids
25
are known. However, it is difficult to determine this last value for organic
Hg
solvents directly, owing to variations in the χ caused by the adsorption
of solvent vapors. 34,54 The simpler and more reliable method is to find the
real energies of solvation from their differences measured relative to
water. 5663 This real medium effect (the real Gibbs energy of ion transfer,
+
+
S
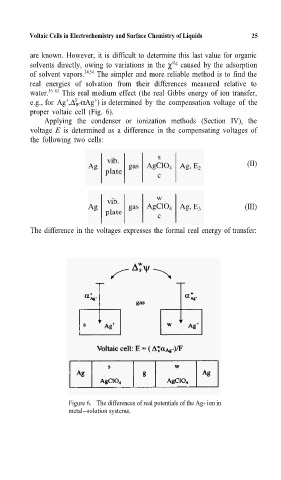
e.g., for Ag ,∆ W αAg ) is determined by the compensation voltage of the
proper voltaic cell (Fig. 6).
Applying the condenser or ionization methods (Section IV), the
voltage E is determined as a difference in the compensating voltages of
the following two cells:
(II)
(III)
The difference in the voltages expresses the formal real energy of transfer:
Figure 6. The differences of real potentials of the Ag+ ion in
metal-solution systems.