Page 42 - MODERN ASPECTS OF ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 42
Voltaic Cells in Electrochemistry and Surface Chemistry of LiquidsA
IX. VOLTAIC CELLS AND ABSOLUTE ELECTRODE 29
POTENTIALS
Knowledge of the Volta potential of a metal/solution interface is relevant
to the interpretation of the absolute electrode potential. According to the
modern view, the relative electrode potential (i.e.,= the emf of a galvanic
cell) measures the value of the energy of the electrons at the Fermi level
of the given metal electrode relative to the metal of the reference electrode.=
On the other hand, considered separately, the absolute value of the
electrode potential measures the woÀ= done in transferring an electron
from a metal surrounded by a macroscopic layer of solution to a point in
a vacuum outside the solotion. 22,72,73
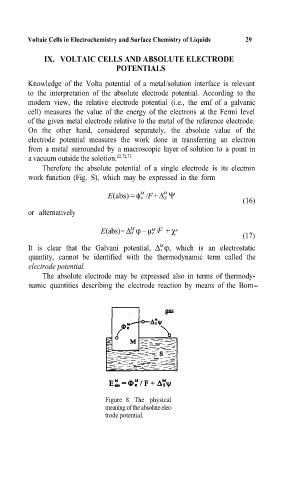
Therefore the absolute potential of a single electrode is its electron
woÀ=function (Fig. S), which may be expressed in the form
E(abs) = φ e /F ∆ S Ψ
M
M
+
(16)
or alternatively
M
E(abs)= ∆ S ϕ –µ /F + χ s
M
e
(17)
M
It is clear that the Galvani potential, ∆ s ϕ, which is an electrostatic
quantity, cannot be identified with the thermodynamic term called the
electrode potential.
The absolute electrode maybe expressed also in terms of thermody-
namic quantities describing the electrode reaction by means of the Born-
Figure 8. The physical
meaning of the absolute elec-
trode potential.