Page 44 - MODERN ASPECTS OF ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 44
Voltaic Cells in Electrochemistry and Surface Chemistry of Liquids
Tùle 1 31
+
Real Free Energy of Solvation of H and *solute Potential ofA
0 ,W
E H (ùs ) in Different Solvents 79
o
-1
Solvent -α o H + (kJ mol ) -E (abs) (V)
Acetone 1118.± 6 4.13±0.06
Acetonitrile 1073.5± 6 4.60 ±0.10
Ethanol 1110.5± 6 4.21± 0.07
Formamide 1102.5± 6 4.29± 0.07
Methaná 1112.5± 6 4.19±0.07
Water 1088.0± 2 4.44± 0.02
X. VOLTA POTENTIALS OFAEX SITU AND NON-SITU
ELECTRODES
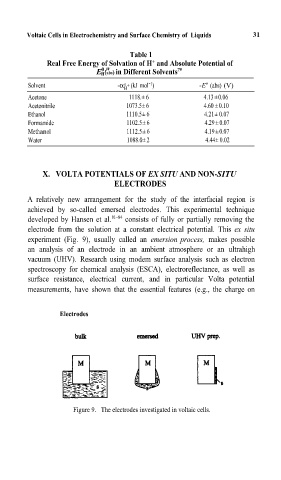
A relatively new arrangement for the study of the interfacial region is
achieved by so-called emersed electrodes.= This experimental technique
developed by Hansen et al. 81–84 consists of fully or partially removing the
electrode from the solution at a constant electrical potential. This ex sit
experiment (Fig. 9), usuallycalled an emersion process, m¸es possiblp
an analysis of an electrode in an ambient atmosphere or an ultrahigh
vacuum (UHV). Research using modem surface analysis such as electron
spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA), electroreflectance, as well as
surface resistance, electrical current, and in particular Volta potential
measurements, have shown that the essential features (e.g.,= the charge on
Electrodes
Figure 9. The electrodes investigated in voltaic cells.=