Page 40 - MODERN ASPECTS OF ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 40
27
Voltaic Cells in Electrochemistry and Surface Chemistry of Liquids
cording to their data, the value of γ * γ* over wide ranges of HCl
1
2
i / i
concentrations does not depend upon the presence of surface-active sub-
stances (e.g., n-heptyl and n-nonyl alcohols) in the experiments.
VIII. REAL POTENTIALS OF IONS IN SOLID
ELECTROLYTES
The possibility of measuring the Volta potential in the system metal–solid-
state electrolyte and using the data obtained to determine ionic compo-
nents of the free lattice energy has been shown in our papers. 67–68 Earlier,
69
Copeland and Seifert measured the Volta potential between Ag and solid
o
AgNø 3 in the temperature range between 190 and 280 C.=They investi-
gated the potential jump during the phase transition from solid to liquid
salt.
M
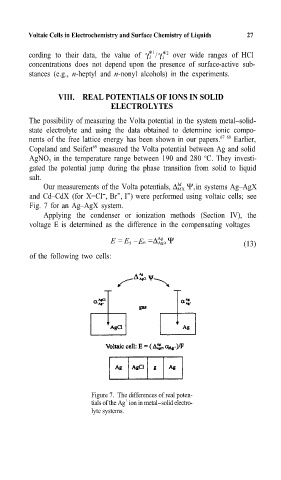
Our measurements of the Volta potentials, ∆ MX Ψ,in systems Ag–AgX
- -
-
and Cd–CdX (for X=Cl ,Br ,I ) were performed using voltaic cells; see
Fig. 7 for an Ag–AgX system.=
Applying the condenser or ionization methods (Section IV),= the
voltage E is determined as the difference in the compensating voltages
Ag
E = E – =∆ Agx Ψ (13)
5 E6
of the following two cells:
Figure 7. The differences of real poten-
+
tials of the Ag ion in metal-solid electro-
lyte systems.=