Page 84 - MODERN ASPECTS OF ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 84
Claude LamyAet al.
68
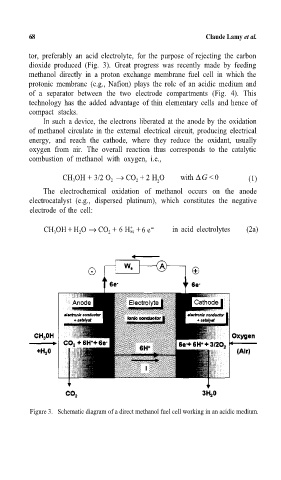
tor, preferably an acid electrolyte, for the purpose of rejecting the carbon
dioxide produced (Fig. 3). Great progress was recently made by feeding
methanol directly in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell in which the
protonic membrane (e.g., Nafion) plays the role of an acidic medium and
of a separator between the two electrode compartments (Fig. 4). This
technology has the added advantage of thin elementary cells and hence of
compact stacks.
In such a device, the electrons liberated at the anode by the oxidation
of methanol circulate in the external electrical circuit, producing electrical
energy, and reach the cathode, where they reduce the oxidant, usually
oxygen from air. The overall reaction thus corresponds to the catalytic
combustion of methanol with oxygen, i.e.,
CH OH + 3/2 O → CO 2 +2 H O with ∆G <0 (1)
3
2
2
The electrochemical oxidation of methanol occurs on the anode
electrocatalyst (e.g., dispersed platinum), which constitutes the negative
electrode of the cell:
+
CH 3 OH + H 2 O → CO 2 +6 Haq 6 e - in acid electrolytes (2a)
+
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of a direct methanol fuel cell working in an acidic medium.