Page 236 -
P. 236
8 The Design Environment 229
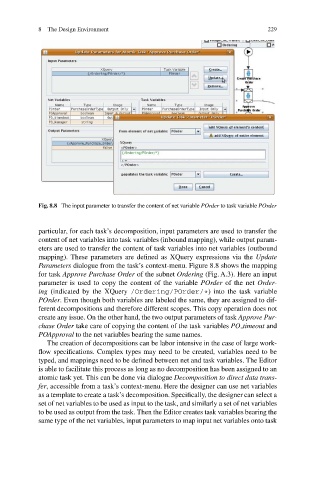
Fig. 8.8 The input parameter to transfer the content of net variable POrder to task variable POrder
particular, for each task’s decomposition, input parameters are used to transfer the
content of net variables into task variables (inbound mapping), while output param-
eters are used to transfer the content of task variables into net variables (outbound
mapping). These parameters are defined as XQuery expressions via the Update
Parameters dialogue from the task’s context-menu. Figure 8.8 shows the mapping
for task Approve Purchase Order of the subnet Ordering (Fig. A.3). Here an input
parameter is used to copy the content of the variable POrder of the net Order-
ing (indicated by the XQuery /Ordering/POrder/ * ) into the task variable
POrder. Even though both variables are labeled the same, they are assigned to dif-
ferent decompositions and therefore different scopes. This copy operation does not
create any issue. On the other hand, the two output parameters of task Approve Pur-
chase Order take care of copying the content of the task variables PO timeout and
POApproval to the net variables bearing the same names.
The creation of decompositions can be labor intensive in the case of large work-
flow specifications. Complex types may need to be created, variables need to be
typed, and mappings need to be defined between net and task variables. The Editor
is able to facilitate this process as long as no decomposition has been assigned to an
atomic task yet. This can be done via dialogue Decomposition to direct data trans-
fer, accessible from a task’s context-menu. Here the designer can use net variables
as a template to create a task’s decomposition. Specifically, the designer can select a
set of net variables to be used as input to the task, and similarly a set of net variables
to be used as output from the task. Then the Editor creates task variables bearing the
same type of the net variables, input parameters to map input net variables onto task