Page 234 -
P. 234
8 The Design Environment 227
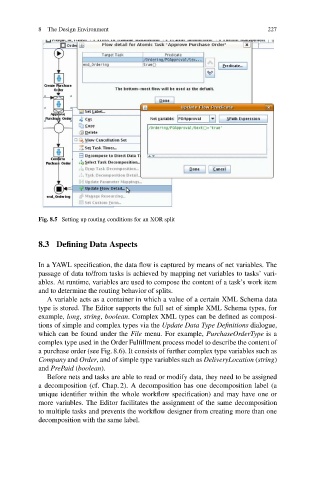
Fig. 8.5 Setting up routing conditions for an XOR split
8.3 Defining Data Aspects
In a YAWL specification, the data flow is captured by means of net variables. The
passage of data to/from tasks is achieved by mapping net variables to tasks’ vari-
ables. At runtime, variables are used to compose the content of a task’s work item
and to determine the routing behavior of splits.
A variable acts as a container in which a value of a certain XML Schema data
type is stored. The Editor supports the full set of simple XML Schema types, for
example, long, string, boolean. Complex XML types can be defined as composi-
tions of simple and complex types via the Update Data Type Definitions dialogue,
which can be found under the File menu. For example, PurchaseOrderType is a
complex type used in the Order Fulfillment process model to describe the content of
a purchase order (see Fig. 8.6). It consists of further complex type variables such as
Company and Order, and of simple type variables such as DeliveryLocation (string)
and PrePaid (boolean).
Before nets and tasks are able to read or modify data, they need to be assigned
a decomposition (cf. Chap. 2). A decomposition has one decomposition label (a
unique identifier within the whole workflow specification) and may have one or
more variables. The Editor facilitates the assignment of the same decomposition
to multiple tasks and prevents the workflow designer from creating more than one
decomposition with the same label.