Page 232 -
P. 232
8 The Design Environment 225
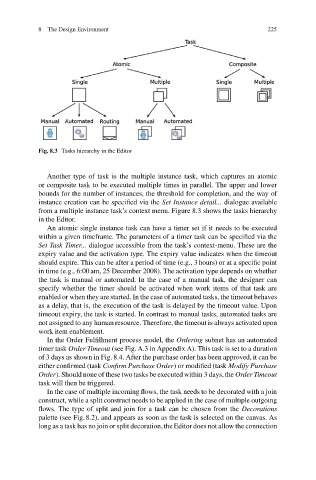
Fig. 8.3 Tasks hierarchy in the Editor
Another type of task is the multiple instance task, which captures an atomic
or composite task to be executed multiple times in parallel. The upper and lower
bounds for the number of instances, the threshold for completion, and the way of
instance creation can be specified via the Set Instance detail... dialogue available
from a multiple instance task’s context menu. Figure 8.3 shows the tasks hierarchy
in the Editor.
An atomic single instance task can have a timer set if it needs to be executed
within a given timeframe. The parameters of a timer task can be specified via the
Set Task Timer... dialogue accessible from the task’s context-menu. These are the
expiry value and the activation type. The expiry value indicates when the timeout
should expire. This can be after a period of time (e.g., 3 hours) or at a specific point
in time (e.g., 6:00 am, 25 December 2008). The activation type depends on whether
the task is manual or automated. In the case of a manual task, the designer can
specify whether the timer should be activated when work items of that task are
enabled or when they are started. In the case of automated tasks, the timeout behaves
as a delay, that is, the execution of the task is delayed by the timeout value. Upon
timeout expiry, the task is started. In contrast to manual tasks, automated tasks are
not assigned to any human resource. Therefore, the timeout is always activated upon
work item enablement.
In the Order Fulfillment process model, the Ordering subnet has an automated
timer task Order Timeout (see Fig. A.3 in Appendix A). This task is set to a duration
of 3 days as shown in Fig. 8.4. After the purchase order has been approved, it can be
either confirmed (task Confirm Purchase Order)ormodified (task Modify Purchase
Order). Should none of these two tasks be executed within 3 days, the Order Timeout
task will then be triggered.
In the case of multiple incoming flows, the task needs to be decorated with a join
construct, while a split construct needs to be applied in the case of multiple outgoing
flows. The type of split and join for a task can be chosen from the Decorations
palette (see Fig. 8.2), and appears as soon as the task is selected on the canvas. As
long as a task has no join or split decoration, the Editor does not allow the connection