Page 153 - Modern Control of DC-Based Power Systems
P. 153
Control Approaches for Parallel Source Converter Systems 117
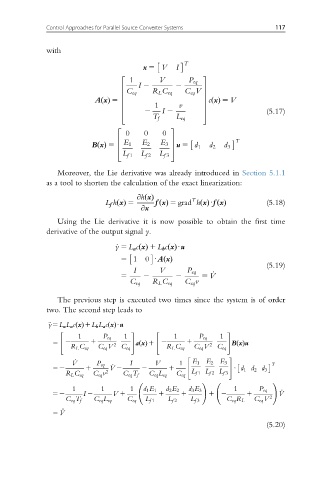
with
T
x 5 V I
2 3
1 V P eq
I 2 2
6 C eq V 7
C eq R L C eq
6 7
AxðÞ 5 6 7 c xðÞ 5 V
6 1 v 7
2 I 2
4 5 (5.17)
T f L eq
2 3
0 0 0
T
E 1 E 2 E 3
6 7
5u 5 d 1 d 2 d 3
BxðÞ 5 4
L f 1 L f 2 L f 3
Moreover, the Lie derivative was already introduced in Section 5.1.1
as a tool to shorten the calculation of the exact linearization:
L f h xðÞ 5 @h xðÞ T (5.18)
@x fxðÞ 5 grad h xðÞUf ðxÞ
Using the Lie derivative it is now possible to obtain the first time
derivative of the output signal y.
_ y 5 L a c xðÞ 1 L b c xðÞUu
5 1 0 UAðxÞ
(5.19)
I V P eq
5 2 2 5 V _
C eq R L C eq C eq v
The previous step is executed two times since the system is of order
two. The second step leads to
ÿ5L a L a c xðÞ1L b L a c xðÞUu
" # " #
1 P eq 1 1 P eq 1
5 2 1 2 axðÞ1 2 1 2 BxðÞu
R L C eq C eq V C eq R L C eq C eq V C eq
" #
_ V I V 1 E 1 E 2 E 3
52 1 P eq 2 _ V 2 2 1 U d 1 d 2 d 3 T
R L C eq C eq v C eq T f C eq L eq C eq L f 1 L f 2 L f 3
! !
1 1 1 d 1 E 1 d 2 E 2 d 3 E 3 1 P eq
52 I 2 V 1 1 1 12 1 _ V
C eq T f C eq L eq C eq L f 1 L f 2 L f 3 C eq R L C eq V 2
5V €
(5.20)