Page 133 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 133
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 56
derivatives produced from DNPH can be separated by the reverse-phase HPLC method [16]. Recently,
Cotrim and others [17] reported the optimum separation conditions for eight types of DNPH derivatives
of aldehydes. The applications of the DNPH method are summarized in Table 1.3.2 [18-23]. In addition,
Karts and others [24] examined in detail the obstructions to separation and detection by by-products
from NO using this method. The use of reagents other than DNPH using 2-diphenylacetyl-1,3-
2
indandion-1-hydrazone (DAIH) and dansyl hydrazine (DNSH) has been reported.
Using the apparatus shown in Fig. 1.3.7, Osaki and others [25] bubbled the nitrogen purge gas from
environmental water and industrial liquid wastes into a DAIH solution, trapped azine compounds
corresponding to acetaldehyde, acrolein, propyonaldehyde and crotonaldehyde, and determined then
using HPLC-FL (Ex. 425 nm, Em. 525 nm). The detection limit was at 1.2 µg/1 in acetaldehyde. Swarin
and others [26] bubbled
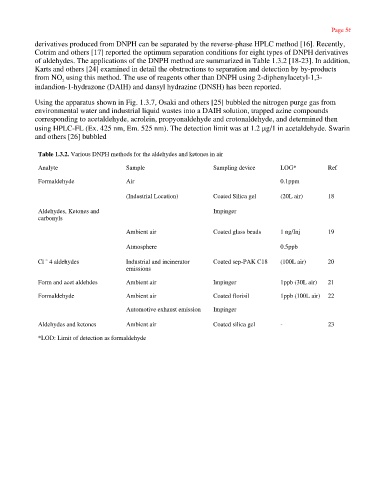
Table 1.3.2. Various DNPH methods for the aldehydes and ketones in air
Analyte Sample Sampling device LOG* Ref
Formaldehyde Air 0.1ppm
(Industrial Location) Coated Silica gel (20L air) 18
Aldehydes, Ketones and Impinger
carbonyls
Ambient air Coated glass beads 1 ng/Inj 19
Atmosphere 0.5ppb
Cl ˜ 4 aldehydes Industrial and incinerator Coated sep-PAK C18 (100L air) 20
emissions
Form and acet aldehdes Ambient air Impinger 1ppb (30L air) 21
Formaldehyde Ambient air Coated florisil 1ppb (100L air) 22
Automotive exhaust emission Impinger
Aldehydes and ketones Ambient air Coated silica gel - 23
*LOD: Limit of detection as formaldehyde
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_56.html 30/09/2003