Page 135 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 135
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 57
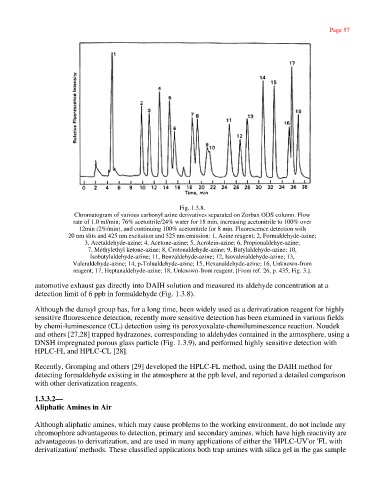
Fig. 1.3.8.
Chromatogram of various carbonyl azine derivatives separated on Zorbax ODS column. Flow
rate of 1.0 ml/min; 76% acetoitrile/24% water for 18 min, increasing acetonitrile to 100% over
12min (2%/min), and continuing 100% acetonitrile for 8 min. Fluorescence detection with
20 nm slits and 425 nm excitation and 525 nm emission: 1, Azine reagent; 2, Formaldehyde-azine;
3, Acetaldehyde-azine; 4, Acetone-azine; 5, Acrolein-azine; 6, Propionaldehye-azine;
7, Methylethyl ketone-azine; 8, Crotonaldehyde-azine; 9, Butylaldehyde-azine; 10,
Isobutylaldehyde-azine; 11, Benzaldehyde-azine; 12, Isovaleraldehyde-azine; 13,
Valeraldehyde-azine; 14, p-Tolualdehyde-azine; 15, Hexanaldehyde-azine; 16, Unknown-from
reagent; 17, Heptanaldehyde-azine; 18, Unknown-from reagent. [From ref. 26, p. 435, Fig. 3.].
automotive exhaust gas directly into DAIH solution and measured its aldehyde concentration at a
detection limit of 6 ppb in formaldehyde (Fig. 1.3.8).
Although the dansyl group has, for a long time, been widely used as a derivatization reagent for highly
sensitive fluorescence detection, recently more sensitive detection has been examined in various fields
by chemi-luminescence (CL) detection using its peroxyoxalate-chemiluminescence reaction. Noudek
and others [27,28] trapped hydrazones, corresponding to aldehydes contained in the atmosphere, using a
DNSH impregnated porous glass particle (Fig. 1.3.9), and performed highly sensitive detection with
HPLC-FL and HPLC-CL [28].
Recently, Gromping and others [29] developed the HPLC-FL method, using the DAIH method for
detecting formaldehyde existing in the atmosphere at the ppb level, and reported a detailed comparison
with other derivatization reagents.
1.3.3.2—
Aliphatic Amines in Air
Although aliphatic amines, which may cause problems to the working environment, do not include any
chromophore advantageous to detection, primary and secondary amines, which have high reactivity are
advantageous to derivatization, and are used in many applications of either the 'HPLC-UV'or 'FL with
derivatization' methods. These classified applications both trap amines with silica gel in the gas sample
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_57.html 30/09/2003