Page 250 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 250
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 116
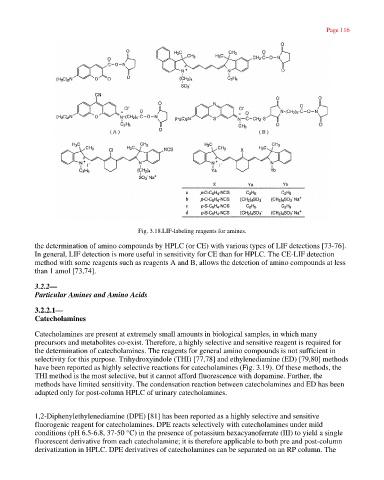
Fig. 3.18.LIF-labeling reagents for amines.
the determination of amino compounds by HPLC (or CE) with various types of LIF detections [73-76].
In general, LIF detection is more useful in sensitivity for CE than for HPLC. The CE-LIF detection
method with some reagents such as reagents A and B, allows the detection of amino compounds at less
than 1 amol [73,74].
3.2.2—
Particular Amines and Amino Acids
3.2.2.1—
Catecholamines
Catecholamines are present at extremely small amounts in biological samples, in which many
precursors and metabolites co-exist. Therefore, a highly selective and sensitive reagent is required for
the determination of catecholamines. The reagents for general amino compounds is not sufficient in
selectivity for this purpose. Trihydroxyindole (THI) [77,78] and ethylenediamine (ED) [79,80] methods
have been reported as highly selective reactions for catecholamines (Fig. 3.19). Of these methods, the
THI method is the most selective, but it cannot afford fluorescence with dopamine. Further, the
methods have limited sensitivity. The condensation reaction between catecholamines and ED has been
adapted only for post-column HPLC of urinary catecholamines.
1,2-Diphenylethylenediamine (DPE) [81] has been reported as a highly selective and sensitive
fluorogenic reagent for catecholamines. DPE reacts selectively with catecholamines under mild
conditions (pH 6.5-6.8, 37-50 °C) in the presence of potassium hexacyanoferrate (III) to yield a single
fluorescent derivative from each catecholamine; it is therefore applicable to both pre and post-column
derivatization in HPLC. DPE derivatives of catecholamines can be separated on an RP column. The
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_116.ht... 30/09/2003