Page 80 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 80
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 30
1.2.4.1—
Sulfonamides
Among widely used chemotherapeutic agents, sulfonamides have a long history and are the most
common veterinary medicine. As for antibacterial residue analysis in foods, considerable research
papers for sulfonamides have been published and most of them use HPLC with UV detection. An
HPLC method with fluorescence derivatization with OPA using pre-column labeling was applied to the
analysis of sulfadimidine and 12 sulfonamides in pork (λex285 nm, λem445 nm) [152,153]. In this
method, the amino group was derivatized under acidic conditions at 60 °C for 30 min without using
active thiol. However, fluorescence derivatization of the amino group with OPA is usually carried out in
alkaline conditions with active thiol. Regarding derivatization with fluorescamine, the use of the pre-
column method for the analysis of 5-8 sulfonamides in meat and milk [154-156], and of the post-
column method for 12 sulfonamides in pork tissues [157] and 14 sulfonamides in salmon tissues [158]
were reported. Also p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde was used for the analysis of six sulfonamides in
liver and kidney of chicken and pig with post-column derivatization monitoring at VIS 450 nm [159].
Detection limits, which differ in samples, for precolumn derivatization with OPA were 0.1-1 ppb and 2-
10 ppb with fluorescamine, proving that derivatization with OPA was more sensitive.
1.2.4.2—
Antibiotics
Penicillin
Penicillins are non-toxic, and used widely in veterinary medicine. However, improper use of the
antibiotics in livestock farming may lead to human hazards. Trace amounts in the livestock food supply
may cause allergic reactions in some individuals.
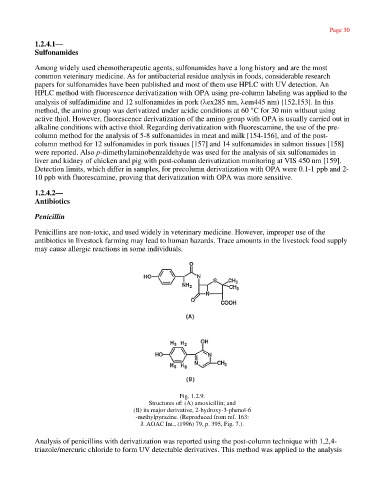
Fig. 1.2.9.
Structures of: (A) amoxicillin; and
(B) its major derivative, 2-hydroxy-3-phenol-6
-methylpyrazine. (Reproduced from ref. 163:
J. AOAC Int., (1996) 79, p. 395, Fig. 7.).
Analysis of penicillins with derivatization was reported using the post-column technique with 1,2,4-
triazole/mercuric chloride to form UV detectable derivatives. This method was applied to the analysis
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_30.html 30/09/2003