Page 82 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 82
Document Página 1 de 1
Page 31
aminocyclitol moiety. Both drugs are approved for use in food-producing animals, and are available in
various formulations for the treatment of a broad spectrum of local and systemic infections. However,
both drugs are potentially toxic by causing damage in vestibular and auditory functions.
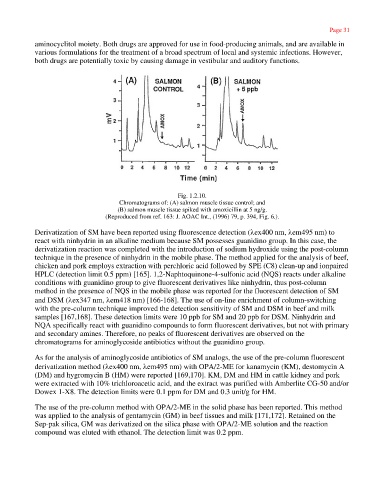
Fig. 1.2.10.
Chromatograms of: (A) salmon muscle tissue control; and
(B) salmon muscle tissue spiked with amoxicillin at 5 ng/g.
(Reproduced from ref. 163: J. AOAC Int., (1996) 79, p. 394, Fig. 6.).
Derivatization of SM have been reported using fluorescence detection (λex400 nm, λem495 nm) to
react with ninhydrin in an alkaline medium because SM possesses guanidino group. In this case, the
derivatization reaction was completed with the introduction of sodium hydroxide using the post-column
technique in the presence of ninhydrin in the mobile phase. The method applied for the analysis of beef,
chicken and pork employs extraction with perchloric acid followed by SPE (C8) clean-up and ionpaired
HPLC (detection limit 0.5 ppm) [165]. 1,2-Naphtoquinone-4-sulfonic acid (NQS) reacts under alkaline
conditions with guanidino group to give fluorescent derivatives like ninhydrin, thus post-column
method in the presence of NQS in the mobile phase was reported for the fluorescent detection of SM
and DSM (λex347 nm, λem418 nm) [166-168]. The use of on-line enrichment of column-switching
with the pre-column technique improved the detection sensitivity of SM and DSM in beef and milk
samples [167,168]. These detection limits were 10 ppb for SM and 20 ppb for DSM. Ninhydrin and
NQA specifically react with guanidino compounds to form fluorescent derivatives, but not with primary
and secondary amines. Therefore, no peaks of fluorescent derivatives are observed on the
chromatograms for aminoglycoside antibiotics without the guanidino group.
As for the analysis of aminoglycoside antibiotics of SM analogs, the use of the pre-column fluorescent
derivatization method (λex400 nm, λem495 nm) with OPA/2-ME for kanamycin (KM), destomycin A
(DM) and hygromycin B (HM) were reported [169,170]. KM, DM and HM in cattle kidney and pork
were extracted with 10% trichloroacetic acid, and the extract was purified with Amberlite CG-50 and/or
Dowex 1-X8. The detection limits were 0.1 ppm for DM and 0.3 unit/g for HM.
The use of the pre-column method with OPA/2-ME in the solid phase has been reported. This method
was applied to the analysis of gentamycin (GM) in beef tissues and milk [171,172]. Retained on the
Sep-pak silica, GM was derivatized on the silica phase with OPA/2-ME solution and the reaction
compound was eluted with ethanol. The detection limit was 0.2 ppm.
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_31.html 30/09/2003