Page 291 - MODERN ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 291
ION–ION INTERACTIONS 227
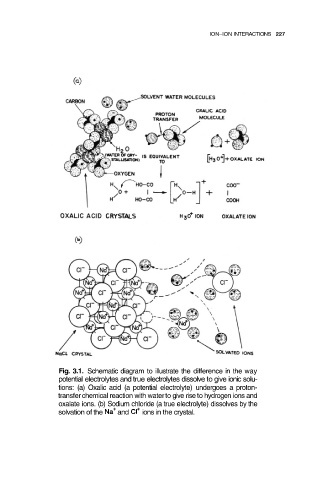
Fig. 3.1. Schematic diagram to illustrate the difference in the way
potential electrolytes and true electrolytes dissolve to give ionic solu-
tions: (a) Oxalic acid (a potential electrolyte) undergoes a proton-
transfer chemical reaction with water to give rise to hydrogen ions and
oxalate ions. (b) Sodium chloride (a true electrolyte) dissolves by the
solvation of the and ions in the crystal.