Page 20 - Modern physical chemistry
P. 20
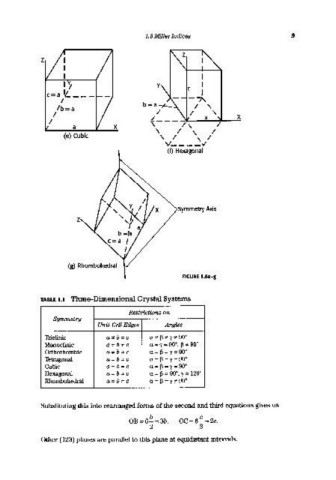
1.8 Miller Indices 9
z
I
I
I
-A
b=a I ,
/ I'
L ___ ~_........;~...a._......;.;;X
a x \ /\
/
\
(e) Cubic \ \ v ____ ..t /
\ I
I
(f) Hexagonal
Symmetry Axis
z
(g) Rhombohedral
FIGURE 1.6e-g
TABLE 1.1 Three-Dimensional Crystal Systems
Restrictions on
Symmetry
Unit-CeU Edges Angles
Triclinic a"¢b"¢c a "¢ p "¢ Y "¢ 90°
Monoclinic a"¢b"¢c a = y = 90°, p"¢ 90°
Orthorhombic a"¢b"¢c a = p = y = 90°
Tetragonal a=b"¢c a=p=y=90°
Cubic a=b=c a=p=y=90°
Hexagonal a=b"¢c a = p = 90°, y = 120°
Rhombohedral a=b=c a=p=y"¢90°
Substituting this into rearranged forms of the second and third equations gives us
b c
OB=6-=3b, OC=6-=2c.
2 3
Other (123) planes are parallel to this plane at equidistant intervals.